If they are bed bug larvae, how do I know for sure. Spotted a few by accident on the frame of my bed, they did not have time to hide, I quickly slapped with my slipper. The only thing that speaks in favor of this opinion is the bites - they are identical to those left by parasites. No adult insects to be found, I looked very carefully. Tell me about the peculiarities of the offspring of bed bugs, please. Respectfully, Lilya.
The author of the portal answers the question:
In my material below, you will learn how to find bed bug larvae, distinguish them from the larvae of other insects, and eradicate them permanently.
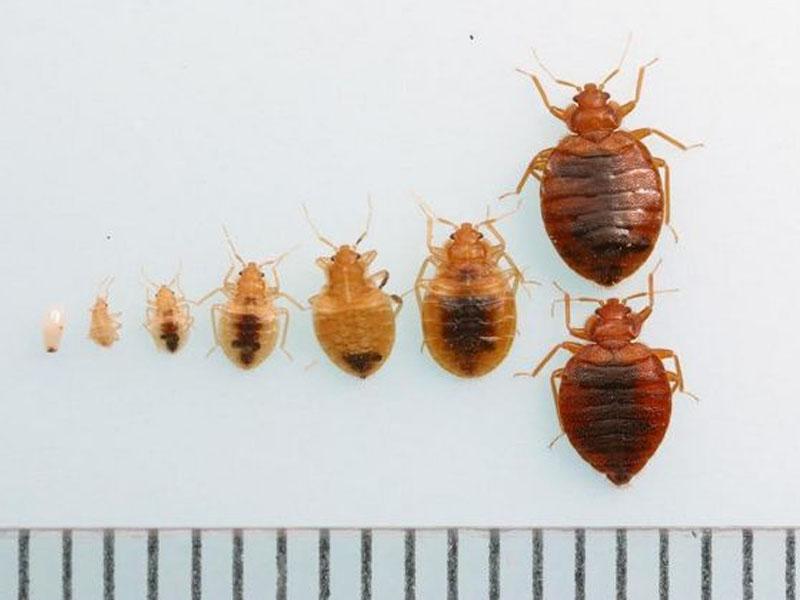
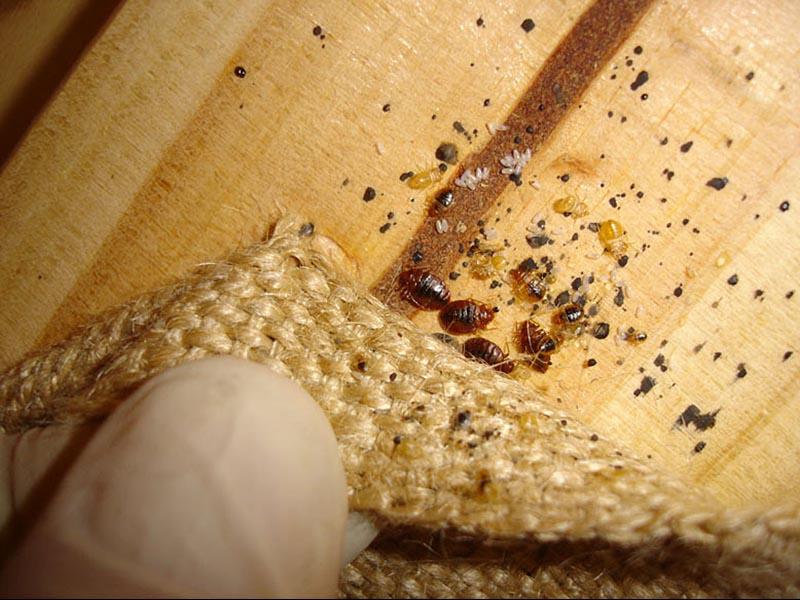
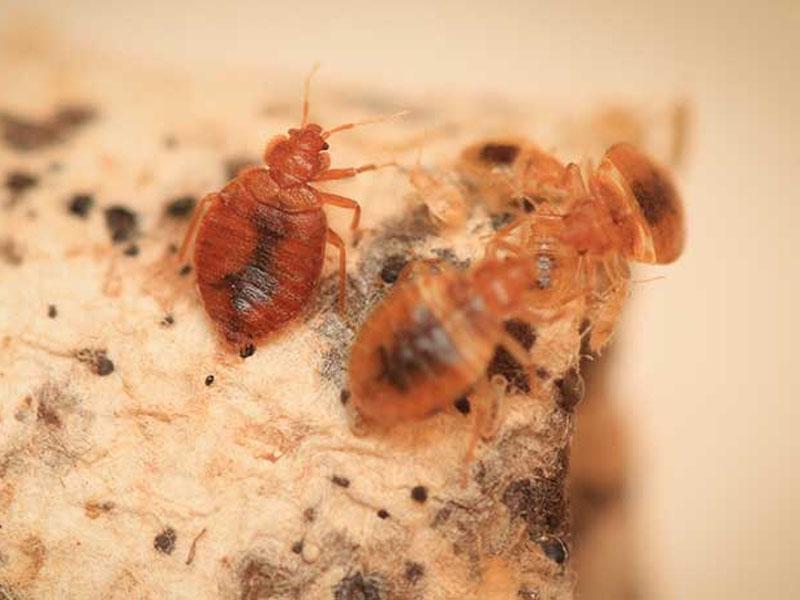
Appearance of house bug larvae. Photo of larvae of sofa, furniture, apartment, linen, bed bugs
Young individuals of blood-sucking insects are called differently. But all the definitions (furniture, linen, couch, apartment) refer to the same type of insects - bed bugs. Popularly, they are called so, given the habitat of the pests found. The larvae of bed bugs look almost the same as the adults of this species:
- The body shape is oval;
- After eating, the color of the chitinous membrane changes - a red tint appears;
- 1 pair of antennae, which allows bed bugs to navigate in space;
- 6 limbs.
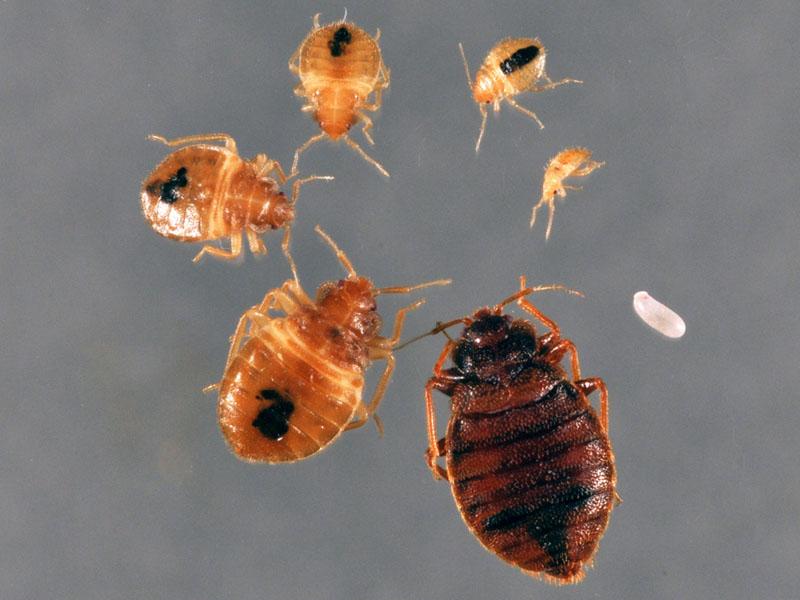
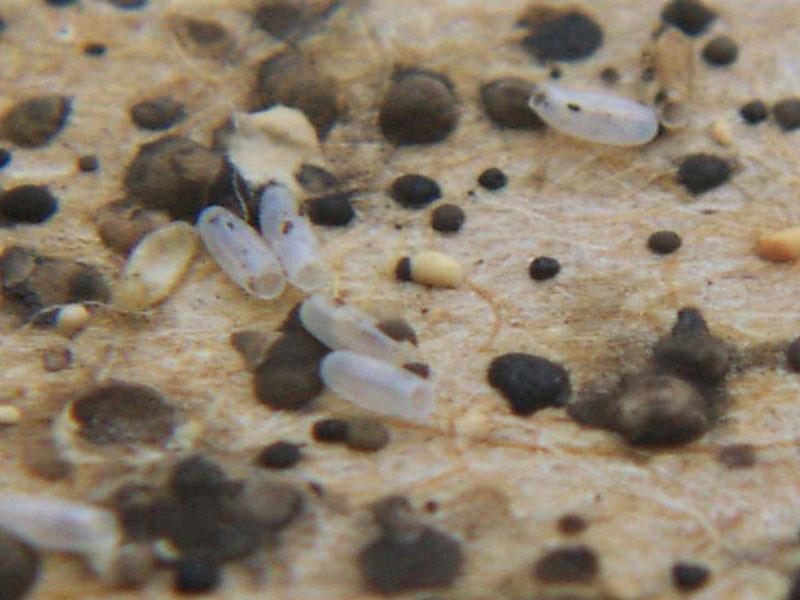
There are also a number of differences between juveniles and adults. To fully form an idea of what bed bug larvae look like, you need to consider the differences as well:
- body length: from 1 to 4 mm, but in fact such an individual passes into the nymphal phase during the first molt, at this stage the size of the insect is smaller (1-2 mm);
- The coloration of the chitinous shell is light: varies from milky white to light brown.
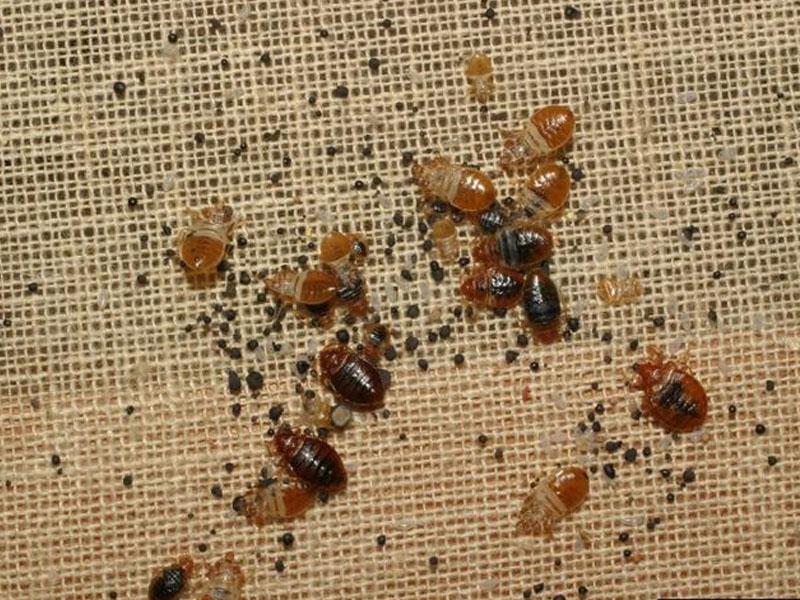
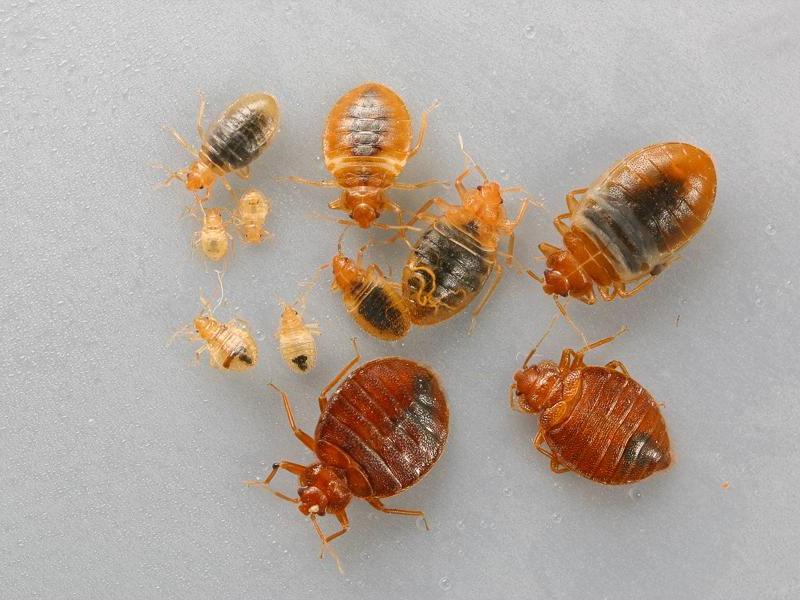

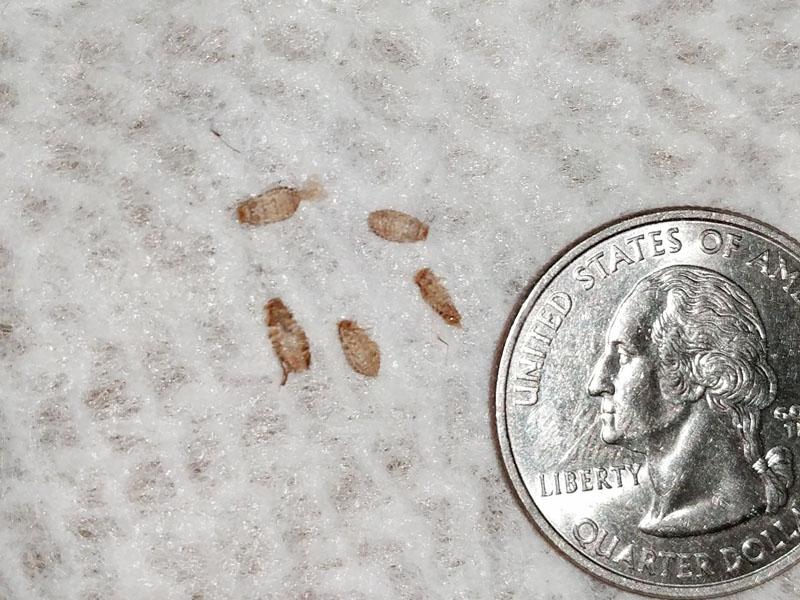

Nutrition and typical habitats of bed bug larvae
Like sexually mature insects, the young require blood to feed. As soon as they emerge from the eggs, they must immediately receive a portion of food. This is the main prerequisite for development parasites. They will not be able to move on to the next stage of formation if they do not receive a portion of food in time. The frequency of feeding of such insects is once every few days.
Moulting occurs immediately after receiving a portion of blood.
Young individuals bite harder than adults. This is due to the not fully developed body: larvae do not yet have the ability to anesthetize the skin puncture site, as adults do. For this reason, they bite more painfully and the unpleasant sensations appear immediately, not after several hours, as after the attack of adults.
The young individuals near humans (their sleeping place) because they move more slowly than adults. It takes them longer to reach the food source at night.
Larvae bedbugs are found in parasite nests, they quietly coexist with sexually mature individuals: inside couches, beds, under baseboards, inside sockets, behind paintings, in books and other places.

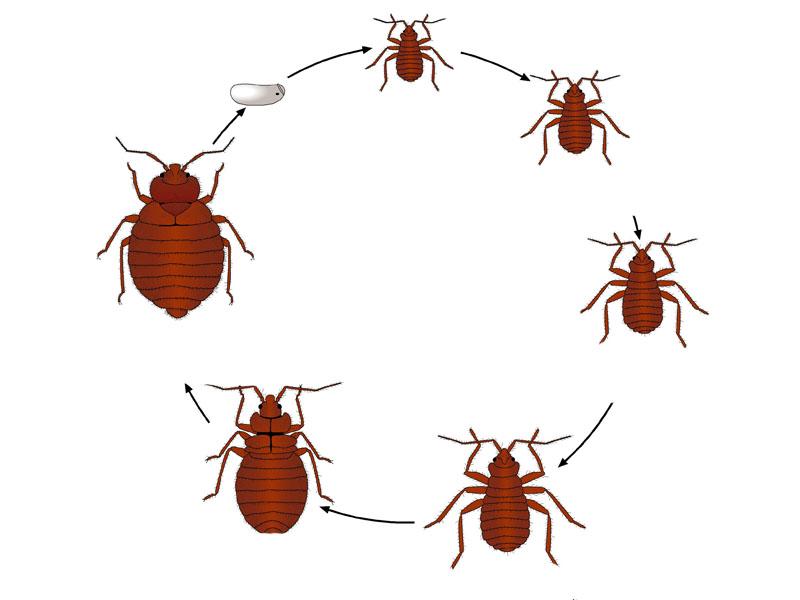
Developmental stages from egg to adult bed bug
There are several main stages:
- maggot emergence from eggs - body length of 1 mm, and the color of the outer covers is milky;
- Nymph - the size of the parasite is 1.5-4 mm, the coloration is darker (from light brown to a more saturated shade);
- adults - body length 5-8 mm, color of outer covers - brown.
The larval cycle includes five stages of molting. This is a natural process of changing appearance and acquiring new body functions. At each of the stages the nymph grows. A developmental jump provides the possibility of an increase of 0.5 mm (average).
Considering that during these stages the appearance of the parasite remains almost the same (except for size and coloration), one can easily imagine what the offspring of bed bugs look like at each stage.

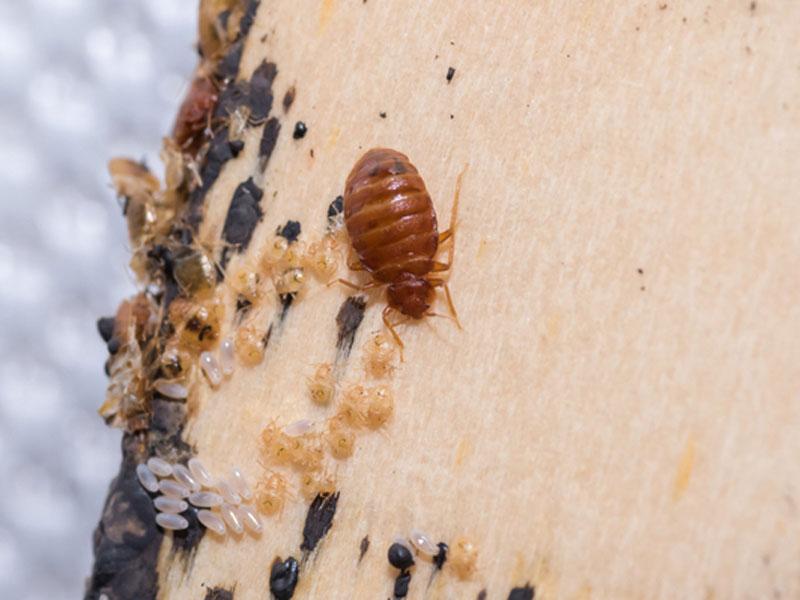
How to distinguish the larvae of bed bugs from those of other insects. How not to confuse with ants, fleas, ticks, and cockroaches
Other insects can also live in the apartment. Among them the most common are: fleas, ants, cockroaches. Mites also attack people, but they are brought in on the body from the street, but these parasites stay longer on the outside. In comparison, bedbugs leave the host immediately after an attack. External signs of different insects to distinguish their offspring from the bedbug larvae:
- Cockroaches: they are larger in size, the body is rounded, the back end is wider, and the color is darker, the antennae are longer, and there are wings;
- mites: body rounded, shield on back, color of outer covers dark, number of limbs - 8, no antennae;
- ants differ primarily in the shape of their bodies - oval, separated by a waist-like structure (a stalk connects the abdomen and thorax);
- fleas: the body is more elongated, flattened not at the top but at the sides, the hind limbs are longer, such insects do not crawl but jump.

Favorable and unfavorable conditions
Domestic parasites prefer comfortable conditions. Nature provides for the possibility of normal development and survival when certain values of environmental parameters are maintained:
- temperature: +20 ... +30°C, with a decrease the development is inhibited, and with an increase - accelerated;
- humidity in the range 50-70, the lower the value of this parameter, the greater the risk of drying out of masonry, and at high humidity actively develop fungus, which contributes to the death of parasites.
Adult bedbug larvae, like those that have just emerged from eggs, cannot normally exist without food. When insects do not receive blood for a long time, they enter the diapause phase, when the organism does not develop.
As a result, the juveniles do not reach the imago stage.

Question and answer section
To understand the best way to deal with house bug larvae, you need to learn more information. If questions arise. You can ask them to a specialist on the website. An entomologist with 19 years of experience answers your questions.
Do bedbug larvae bite humans?

How many larvae does a bedbug lay?

At what temperature do bedbug larvae die?

How long does a bedbug larva live?

What does a bedbug larva bite look like?

How long do bed bug larvae live without food?

How to reliably get rid of bed bugs, including their larvae and eggs - ways to affect the insects and their offspring
Consider opportunities that contribute to pest elimination:
- temperature effect is the most effective way to kill the offspring of bed bugs because the insects die at all stages if the air temperature is above +55°C and below -25°C almost instantly, the developing organisms inside the eggs also die;
- chemicals: different kinds of insecticides are used, all of which help to kill the larvae, but only some of which can kill the eggs.
It should be understood that you can get rid of bed bugs quickly by temperature exposure only in conditions where the temperature reaches extreme values.
Intermediates also have a devastating effect on parasites, but it takes some time to achieve the desired result: from a few hours to 1-3 days.
Mechanical methods do not guarantee complete destruction of the colony, because the chitinous covers and the shell of the eggs protect the offspring from damage. Folk remedies also do not always kill larvae and eggs. The death of the offspring occurs only if they come into contact with a large amount of a poisonous substance.

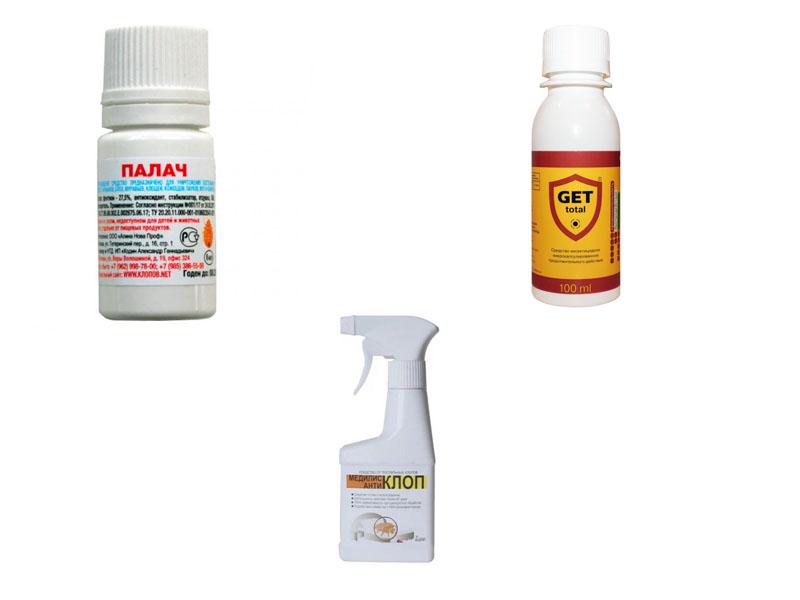
Effective strong remedies to get rid of bed bug larvae
Household insecticides are a reliable way to control parasites. Even if non-ovicidal preparations are used, the offspring will not live long anyway. Death occurs after emergence from the eggs, as the young come into contact with the insecticide that was previously sprayed over surfaces. Bed bug killing agents:
- The Executioner - concentrated liquid, used to prepare a working solution, can kill bed bugs for several weeks after treatment because it has a prolonged effect;
- Get - microencapsulated product, due to the structure of the poison is released over a long period, which means that the product will remain active for a long time, which will ensure the death of all individuals that have emerged from the eggs;
- Medilis-AnticlopThe pesticides continue to kill pests at any stage of development for 60 days, which ensures the death of the entire colony of parasites.

Folk analogues of the effect on insects
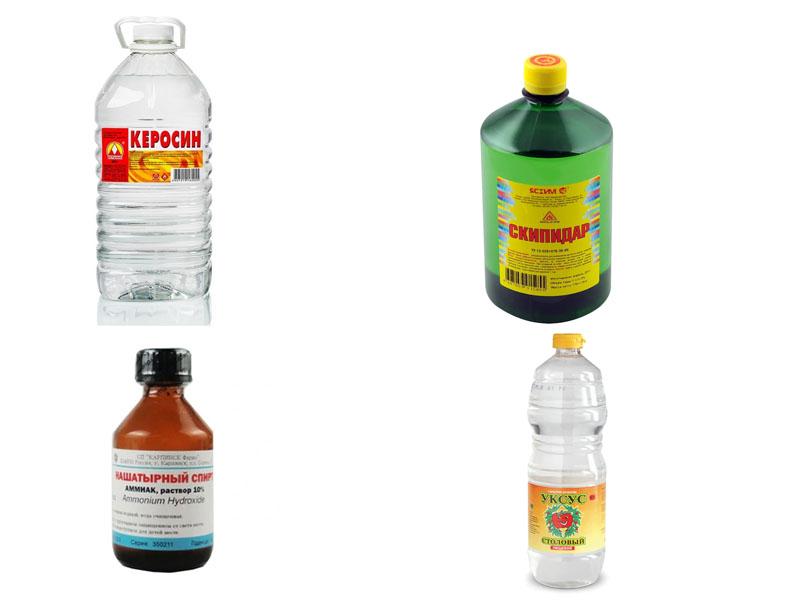
If you flood the nest with one of the following substances, the insects at any stage of development will not survive:
- kerosene - in a water solution repels insects, so it is recommended to use a concentrated substance, but then the smell remains;
- turpentine - acts destructively in combination with other means (naphthalene, denatured alcohol);
- Ammonia is a strong smelling agent that, when added to the floor cleaning water, will scare away the larvae, and if you pour it into a bedbug nest, it will kill them;
- ethyl alcohol - used to kill insects that congregate inside furniture;
- Vinegar - acts like other household chemicals, but in diluted form it is less effective.

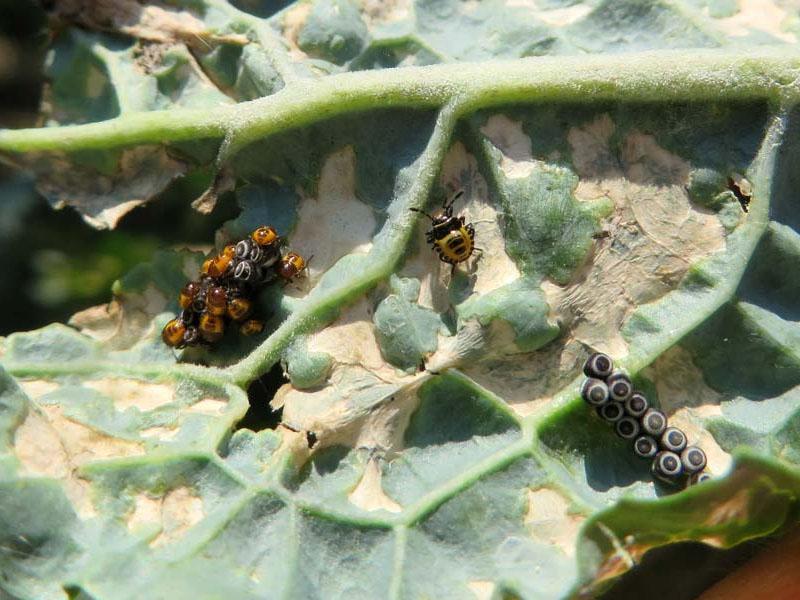
Street bugs and their larvae
In appearance, the young of most pests of different species and adult insects are often similar. They differ in color and size. Features of street bugs of different species found in the garden, in the homestead, in parks:
- "soldier": larvae are red, black pattern appears after several molts;
- "stinker.": The color of the outer covers changes at each stage of molting (red-orange, black, brown-white);
- "turtle.": Shades of outer covers constantly change after each molt (light pink, dark brown, yellow-gray, brown-gray);
- watermakerBody yellow, then it darkens, the size of the parasite immediately after emergence from the egg is small, the young look more bloated;
- triatomous: larvae have no wings, body length - 2 mm, for comparison, adult parasites reach 35 mm, can fly.

Feedback on the encounter with maggots
Expert tips

- The young have an insufficiently powerful mouthpiece, but they still bite humans; in comparison, the offspring of other species of bed bugs attack large warm-blooded creatures, having moved on to the last stage of development, and before that they bite small animals;
- The methods of combating juveniles do not differ from those used to kill adult parasites, but the death of larvae comes much faster.

Conclusion
Young bedding pests have much in common with adults. They differ only in coloration and body size. In this case, the chitinous shell does not change color too much (from light brown to darker in the same color range). Specimens of other species differ more strongly at the initial stage of development. Changes in coloration in different tones are observed. Other features of the larvae:
- Bedworms strive to be as close to humans as possible. They live in the same nests as adults - all insects feed on blood and cannot normally exist without it.
- Larvae go through several developmental stages. When they reach the nymphal phase, they change their chitinous coverings 5 times, which allows them to grow.
- Conditions favor development: temperature within +20° ... 30°С, air humidity 50-70. It is important that the source of food is always near, because without blood the insects fall into an anabiosis-like state (diapause).

